Here's what you need. Make sure that your PC or Microsoft Surface is updated to the latest version of Windows 10. Have your Apple ID and password ready. If you don't have an Apple ID, you can create one. On Windows 7 and Windows 8, you can download iCloud for Windows on Apple's website. Nov 12, 2020 Install hping3 For CentOS, Fedora, RHEL The rpm based distirubtions like CentOS, Fedora, RHEL provides the hping with the name of hping3. The hping3 package can be installed with the following command for these distributions. $ sudo yum install hping3.
Table of ContentsName
hping2 - send (almost) arbitrary TCP/IP packets to network hostsSynopsis
hping2[ -hvnqVDzZ012WrfxykQbFSRPAUXYjJBuTG ] [ -ccount ] [ -iwait ] [ --fast ] [-Iinterface ] [ -9signature ] [ -ahost ] [ -tttl ] [ -Nip id ] [ -Hip protocol] [ -g fragoff ] [ -mmtu ] [ -otos ] [
fragoff ] [ -mmtu ] [ -otos ] [  -Cicmp type ] [
-Cicmp type ] [ Install Hping3 On Windows 8
-Kicmp code ] [ -ssource port ] [ -p[+][+]dest port ] [ -wtcp window ] [ -Otcp offset ] [-Mtcp sequence number ] [ -Ltcp ack ] [ -ddata size ] [ -Efilename ] [-esignature ] [ --icmp-ipverversion ] [ --icmp-iphlenlength ] [ --icmp-iplenlength] [ --icmp-ipidid ] [ --icmp-ipprotoprotocol ] [ --icmp-cksumchecksum ] [ --icmp-ts] [ --icmp-addr ] [ --tcpexitcode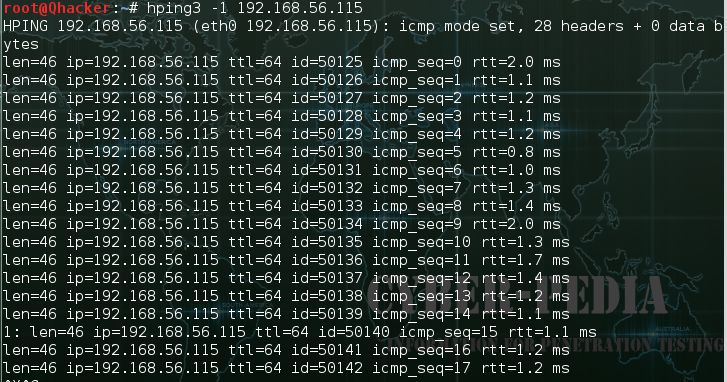 ] [ --tcp-timestamp ] [ --tr-stop ] [ --tr-keep-ttl] [ --tr-no-rtt ] hostname
] [ --tcp-timestamp ] [ --tr-stop ] [ --tr-keep-ttl] [ --tr-no-rtt ] hostname 
Description
hping2 is a network tool able to send custom TCP/IP packetsand to display target replies like ping program does with ICMP replies.hping2 handle fragmentation, arbitrary packets body and size and can beused in order to transfer files encapsulated under supported protocols.Using hping2 you are able to perform at least the following stuff: - Testfirewall rules
- Advanced port scanning
- Test net performance using different protocols,
packet size, TOS (type of service) and fragmentation.
- Path MTU discovery
- Transferring files between even really fascist firewall
rules.
- Traceroute-like under different protocols.
- Firewalk-like usage.
- Remote OS fingerprinting.
- TCP/IP stack auditing.
- A lot of others.
It's also a good didactic tool to learn TCP/IP. hping2 is developed andmaintained by antirez@invece.org and is licensed under GPL version 2. Developmentis open so you can send me patches, suggestion and affronts without inhibitions.
Hping Site
primary site at http://www.hping.org You can found both the stablerelease and the istruction to download the latest source code at http://www.hping.org/download.htmlBase Options
len=46 ip=192.168.1.1 flags=RA DF seq=0 ttl=255 id=0 win=0 rtt=0.4 ms tos=0iplen=40 seq=0 ack=1380893504 sum=2010 urp=0
Protocol Selection
Default protocol is TCP, by default hping2 will sendtcp headers to target host's port 0 with a winsize of 64 without any tcpflag on. Often this is the best way to do an 'hide ping', useful when targetis behind a firewall that drop ICMP. Moreover a tcp null-flag to port 0 hasa good probability of not being logged.- -0 --rawip
- RAW IP mode, in this modehping2 will send IP header with data appended with --signature and/or --file,see also --ipproto that allows you to set the ip protocol field.
- -1 --icmp
- ICMPmode, by default hping2 will send ICMP echo-request, you can set other ICMPtype/code using --icmptype --icmpcode options.
- -2 --udp
- UDP mode, by default hping2will send udp to target host's port 0. UDP header tunable options are thefollowing: --baseport, --destport, --keep.
- -9 --listen signature
- HPING2 listen mode,using this option hping2 waits for packet that contain signature and dumpfrom signature end to packet's end. For example if hping2 --listen TEST readsa packet that contain 234-09sdflkjs45-TESThello_world it will display hello_world.
Ip Related Options
- -a --spoof hostname
- Use this option in order to set a fakeIP source address, this option ensures that target will not gain your realaddress. However replies will be sent to spoofed address, so you will can'tsee them. In order to see how it's possible to perform spoofed/idle scanningsee the HPING2-HOWTO.
- -t --ttl time to live
- Using this option you can set TTL(time to live) of outgoing packets, it's likely that you will use this with--traceroute or --bind options. If in doubt try ` hping2 some.host.com -t 1 --traceroute'.
- -N --id
- Set ip->id field. Default id is random but if fragmentation is turnedon and id isn't specified it will be getpid() & 0xFF , to implement a bettersolution is in TODO list.
- -H --ipproto
- Set the ip protocol in RAW IP mode.
- -W--winid
- Windows* id has different byte ordering, if this option is enablehping2 will properly display windows reply ids.
- -r --rel
- Display id incrementsinstead of id. See the HPING2-HOWTO for more information. Increments aren'tcomputed as id[N]-id[N-1] but using packet loss compensation. See relid.c formore information.
- -f --frag
- Split packets in more fragments, this may be usefulin order to test IP stacks fragmentation performance and to test if somepacket filter is so weak that can be passed using tiny fragments (anachronistic).Default 'virtual mtu' is 16 bytes. see also --mtu option.
- -x --morefrag
- Set morefragments IP flag, use this option if you want that target host send anICMP time-exceeded during reassembly.
- -y --dontfrag
- Set don't fragment IP flag,this can be used to perform MTU path discovery.
- -g --fragoff fragment offsetvalue
- Set the fragment offset
- -m --mtu mtu value
- Set different 'virtual mtu'than 16 when fragmentation is enabled. If packets size is greater that 'virtualmtu' fragmentation is automatically turned on.
- -o --tos hex_tos
- Set Type OfService (TOS) , for more information try --tos help
- -G --rroute
- Record route.Includes the RECORD_ROUTE option in each packet sent and displays the routebuffer of returned packets. Note that the IP header is only large enoughfor nine such routes. Many hosts ignore or discard this option. Also notethat using hping you are able to use record route even if target host filterICMP. Record route is an IP option, not an ICMP option, so you can use recordroute option even in TCP and UDP mode.
Icmp Related Options
- -C --icmptype type
- Set icmp type, default is ICMP echo request (implies --icmp)
- -K --icmpcode code
- Set icmp code, default is 0. (implies --icmp)
- --icmp-ipver
- Set IP version ofIP header contained into ICMP data, default is 4.
- --icmp-iphlen
- Set IP headerlength of IP header contained into ICMP data, default is 5 (5 word of 32bits).
- --icmp-iplen
- Set IP packet length of IP header contained into ICMP data,default is the real length.
- --icmp-ipid
- Set IP id of IP header contained intoICMP data, default is random.
- --icmp-ipproto
- Set IP protocol of IP header containedinto ICMP data, default is TCP.
- --icmp-cksum
- Set ICMP checksum, for defaultis the valid checksum.
- --icmp-ts
- Alias for --icmptype 13 (to send ICMP timestamprequests)
- --icmp-addr
- Alias for --icmptype 17 (to send ICMP address mask requests)
Tcp/Udp Related Options
Install Hping3 On Windows Download
#hping2 win98--seqnum -p 139 -S -i u1 -I eth0
HPING uaz (eth0 192.168.4.41): S set, 40 headers + 0 data bytes
2361294848 +2361294848
2411626496 +50331648
2545844224 +134217728
2713616384 +167772160
2881388544 +167772160
3049160704 +167772160
3216932864 +167772160
3384705024 +167772160
3552477184 +167772160
3720249344 +167772160
3888021504 +167772160
4055793664 +167772160
4223565824 +167772160
The first column reports the sequence number, the second difference betweencurrent and last sequence number. As you can see target host's sequence numbersare predictable.

Common Options
- -d --data data size
- set packet body size. Warning,using --data 40 hping2 will not generate 0 byte packets but protocol_header+40bytes. hping2 will display packet size information as first line output,like this: HPING www.yahoo.com (ppp0 204.71.200.67): NO FLAGS are set, 40 headers+ 40 data bytes
- -E --file filename
- Use filename contents to fill packet's data.
- -e --sign signature
- Fill first signature length bytes of data with signature.If signature length is bigger than data size an error message will be displayed.This option can be used safely with --file filename option, remainder dataspace will be filled using filename
- -j --dump
- Dump received packets in hex.
- -J --print
- Dump received packets's printable characters.
- -B --safe
- Enable safeprotocol, using this option lost packets in file transfers will be resent.For example in order to send file /etc/passwd from host A to host B youmay use the following:
[host_a]# hping2 host_b --udp -p 53 -d 100 --sign signature --safe --file /etc/passwd
[host_b]# hping2 host_a --listen signature --safe --icmp - -u --end
- If you are using --file filenameoption, tell you when EOF has been reached. Moreover prevent that otherend accept more packets. Please, for more information see the HPING2-HOWTO.
- -T --traceroute
- Traceroute mode. Using this option hping2 will increase ttlfor each ICMP time to live 0 during transit received. Try hping2 host --traceroute.This option implies --bind and --ttl 1. You can override the ttl of 1 usingthe --ttl option. Since 2.0.0 stable it prints RTT information.
- --tr-keep-ttl
- Keepthe TTL fixed in traceroute mode, so you can monitor just one hop in theroute. For example, to monitor how the 5th hop changes or how its RTT changesyou can try hping2 host --traceroute --ttl 5 --tr-keep-ttl.
- --tr-stop
- If this optionis specified hping will exit once the first packet that isn't an ICMP timeexceeded is received. This better emulates the traceroute behavior.
- --tr-no-rtt
- Don't show RTT information in traceroute mode. The ICMP time exceeded RTTinformation aren't even calculated if this option is set.
- --tcpexitcode
- Exitwith last received packet tcp->th_flag as exit code. Useful for scripts thatneed, for example, to known if the port 999 of some host reply with SYN/ACKor with RST in response to SYN, i.e. the service is up or down.
Tcp OutputFormat
The standard TCP output format is the following:len=46 ip=192.168.1.1
flags=RA DF seq=0 ttl=255 id=0 win=0 rtt=0.4 ms
len is the size, in bytes,of the data captured from the data link layer excluding the data link headersize. This may not match the IP datagram size due to low level transportlayer padding.
ip is the source ip address.
flags are the TCP flags, Rfor RESET, S for SYN, A for ACK, F for FIN, P for PUSH, U for URGENT, Xfor not standard 0x40, Y for not standard 0x80.
If the reply contains DFthe IP header has the don't fragment bit set.
seq is the sequence numberof the packet, obtained using the source port for TCP/UDP packets, thesequence field for ICMP packets.
id is the IP ID field.
win is the TCPwindow size.
rtt is the round trip time in milliseconds.
If you run hpingusing the -V command line switch it will display additional informationabout the packet, example:
len=46 ip=192.168.1.1 flags=RA DF seq=0 ttl=255id=0 win=0 rtt=0.4 ms tos=0 iplen=40 seq=0 ack=1223672061 sum=e61d urp=0
tos is the type of service field of the IP header.
iplen is the IP total
len field
seq and ack are the sequence and acknowledge 32bit numbers inthe TCP header.
sum is the TCP header checksum value
urp is the TCP urgent
pointer value
Udp Output Format
The standard output format is:
len=46
ip=192.168.1.1 seq=0 ttl=64 id=0 rtt=6.0 ms
The field meaning is just thesame as the TCP output meaning of the same fields.
Icmp Output Format
Anexample of ICMP output is:
ICMP Port Unreachable from ip=192.168.1.1 name=nano.marmoc.net
It is very simple to undestand. It starts with the string 'ICMP' followedby the description of the ICMP error, Port Unreachable in the example. Theip field is the IP source address of the IP datagram containing the ICMPerror, the name field is just the numerical address resolved to a name(a dns PTR request).
The ICMP Time exceeded during transit or reassemblyformat is a bit different:
TTL 0 during transit from ip=192.168.1.1 name=nano.marmoc.net
The only difference is the description of the error, it starts with TTL0.
Author
Salvatore Sanfilippo <antirez@invece.org>, with the help of the peoplementioned in AUTHORS file and at http://www.hping.org/authors.htmlBugs
Evenusing the --end and --safe options to transfer files the final packet willbe padded with 0x00 bytes.Data is read without care about alignment, butalignment is enforced in the data structures. This will not be a problemunder i386 but, while usually the TCP/IP headers are naturally aligned,may create problems with different processors and bogus packets if thereis some unaligned access around the code (hopefully none).